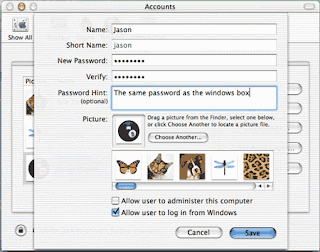
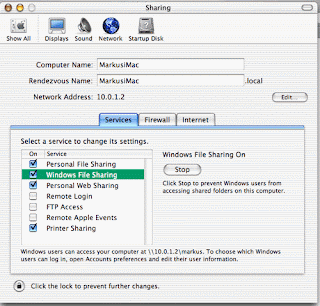
Useful Run Commands for Windows Accessibility Controls -access.cpl
Add Hardware Wizard-hdwwiz.cpl
Add/Remove Programs-appwiz.cpl
Administrative Tools-control admintools
Automatic Updates-wuaucpl.cpl
Bluetooth Transfer Wizard-fsquirt
Calculator-calc
Certificate Manager-certmgr.ms
Character Map-charmap
Check Disk Utility-chkdsk
Clipboard Viewer-clipbrd
Command Prompt-cmd
Component Services-dcomcnfg
Computer Management-compmgmt.msc
Date and Time Properties-timedate.cpl
DDE Shares-ddeshare
Device Manager-devmgmt.msc
Direct X Control Panel (If Installed)-directx.cpl
Direct X Troubleshooter-dxdiag
Disk Cleanup Utility-cleanmgr
Disk Defragment-dfrg.msc
Disk Management-diskmgmt.msc
Disk Partition Manager-diskpart
Display Properties-control desktop
Display Properties-desk.cpl
Display Properties (w/Appearance Tab Preselected)-control color
Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility-drwtsn32
Driver Verifier Utility-verifier
Event Viewer-eventvwr.msc
File Signature Verification Tool-sigverif
Findfast-findfast.cpl
Folders Properties-control folders
Fonts-control fonts
Fonts Folder-fonts
Free Cell Card Game-freecell
Game Controllers-joy.cpl
Group Policy Editor (XP Prof)-gpedit.msc
Hearts Card Game-mshearts
Iexpress Wizard-iexpress
Indexing Service-ciadv.msc
Internet Properties-inetcpl.cpl
IP Configuration (Display Connection Configuration)-ipconfig /all
IP Configuration (Display DNS Cache Contents)-ipconfig /displaydns
IP Configuration (Delete DNS Cache Contents)-ipconfig /flushdns
IP Configuration (Release All Connections)-ipconfig /release
IP Configuration (Renew All Connections)-pconfig /renew
IP Configuration (Refreshes DHCP & Re-Registers DNS)-ipconfig /registerdns
IP Configuration (Display DHCP Class ID)-ipconfig /showclassid
IP Configuration (Modifies DHCP Class ID)-ipconfig /setclassid
Java Control Panel (If Installed)-jpicpl32.cpl
Java Control Panel (If Installed)-javaws
Keyboard Properties-control keyboard
Local Security Settings-secpol.msc
Local Users and Groups-lusrmgr.msc
Logs You Out Of Windows-logoff
Microsoft Chat-winchat
Minesweeper Game-winmine
Mouse Properties-control mouse
Mouse Properties-main.cpl
Network Connections-control netconnections
Network Connections-ncpa.cpl
Network Setup Wizard-netsetup.cpl
Notepad-notepad
Nview Desktop Manager(If Installed)-nvtuicpl.cpl
Object Packager-packager
ODBC Data Source Administrator-odbccp32.cpl
On Screen Keyboard-osk
Opens AC3 Filter (If Installed)-ac3filter.cpl
Password Properties-password.cpl
Performance Monitor-perfmon.msc
Performance Monitor-perfmon
Phone and Modem Options-telephon.cpl
Power Configuration-powercfg.cpl
Printers and Faxes-control printers
Printers Folder-printers
Private Character Editor-eudcedit
Quicktime (If Installed)-QuickTime.cpl
Regional Settings-intl.cpl
Registry Editor-regedit
Registry Editor-regedit32
Remote Desktop-mstsc
Removable Storage-ntmsmgr.msc
Removable Storage Operator Requests-ntmsoprq.msc
Resultant Set of Policy (XP Prof)-rsop.msc
Scanners and Cameras-sticpl.cpl
Scheduled Tasks-control schedtasks
Security Center-wscui.cpl
Services-services.msc
Shared Folders-fsmgmt.msc
Shuts Down Windows-shutdown
Sounds and Audio-mmsys.cpl
Spider Solitare Card Game-spider
SQL Client Configuration-cliconfg
System Configuration Editor-sysedit
System Configuration Utility-msconfig
System File Checker Utility (Scan Immediately)-sfc /scannow
System File Checker Utility (Scan Once At Next Boot)-sfc /scanonce
System File Checker Utility (Scan On Every Boot)-sfc /scanboot
System File Checker Utility (Return to Default Setting)-sfc /revert
System File Checker Utility (Purge File Cache)-sfc /purgecache
System File Checker Utility (Set Cache Size to size x)-sfc /cachesize=x
System Properties-sysdm.cpl
Task Manager-taskmgr
Telnet Client-telnet
User Account Management-nusrmgr.cpl
Utility Manager-utilman
Windows Firewall-firewall.cpl
Windows Magnifier-magnify
Windows Management Infrastructure-wmimgmt.msc
Windows System Security Tool-syskey
Windows Update Launches-wupdmgr
Windows XP Tour Wizard-tourstart
Wordpad-write
A-Z Index of the Windows XP command line
ADDUSERS Add or list users to/from a CSV file
ARP Address Resolution Protocol
ASSOC Change file extension associations
ASSOCIAT One step file association
AT Schedule a command to run at a later time
ATTRIB Change file attributes
BOOTCFG Edit Windows boot settings
BROWSTAT Get domain, browser and PDC info
CACLS Change file permissions
CALL Call one batch program from another
CD Change Directory - move to a specific Folder
CHANGE Change Terminal Server Session properties
CHKDSK Check Disk - check and repair disk problems
CHKNTFS Check the NTFS file system
CHOICE Accept keyboard input to a batch file
CIPHER Encrypt or Decrypt files/folders
CleanMgr Automated cleanup of Temp files, recycle bin
CLEARMEM Clear memory leaks
CLIP Copy STDIN to the Windows clipboard.
CLS Clear the screen
CLUSTER Windows Clustering
CMD Start a new CMD shell
COLOR Change colors of the CMD window
COMP Compare the contents of two files or sets of files
COMPACT Compress files or folders on an NTFS partition
COMPRESS Compress individual files on an NTFS partition
CON2PRT Connect or disconnect a Printer
CONVERT Convert a FAT drive to NTFS.
COPY Copy one or more files to another location
CSCcmd Client-side caching (Offline Files)
CSVDE Import or Export Active Directory data
DATE Display or set the date
Dcomcnfg DCOM Configuration Utility
DEFRAG Defragment hard drive
DEL Delete one or more files
DELPROF Delete NT user profiles
DELTREE Delete a folder and all subfolders
DevCon Device Manager Command Line Utility
DIR Display a list of files and folders
DIRUSE Display disk usage
DISKCOMP Compare the contents of two floppy disks
DISKCOPY Copy the contents of one floppy disk to another
DNSSTAT DNS Statistics
DOSKEY Edit command line, recall commands, and create macros
DSADD Add user (computer, group..) to active directory
DSQUERY List items in active directory
DSMOD Modify user (computer, group..) in active directory
ECHO Display message on screen
ENDLOCAL End localisation of environment changes in a batch file
ERASE Delete one or more files
EXIT Quit the CMD shell
EXPAND Uncompress files
EXTRACT Uncompress CAB files
FC Compare two files
FDISK Disk Format and partition
FIND Search for a text string in a file
FINDSTR Search for strings in files
FOR /F Loop command: against a set of files
FOR /F Loop command: against the results of another command
FOR Loop command: all options Files, Directory, List
FORFILES Batch process multiple files
FORMAT Format a disk
FREEDISK Check free disk space (in bytes)
FSUTIL File and Volume utilities
FTP File Transfer Protocol
FTYPE Display or modify file types used in file extension associations
GLOBAL Display membership of global groups
GOTO Direct a batch program to jump to a labelled line
HELP Online Help
HFNETCHK Network Security Hotfix Checker
IF Conditionally perform a command
IFMEMBER Is the current user in an NT Workgroup
IPCONFIG Configure IP
KILL Remove a program from memory
LABEL Edit a disk label
LOCAL Display membership of local groups
LOGEVENT Write text to the NT event viewer.
LOGOFF Log a user off
LOGTIME Log the date and time in a file
MAPISEND Send email from the command line
MEM Display memory usage
MD Create new folders
MKLINK Create a symbolic link (linkd)
MODE Configure a system device
MORE Display output, one screen at a time
MOUNTVOL Manage a volume mount point
MOVE Move files from one folder to another
MOVEUSER Move a user from one domain to another
MSG Send a message
MSIEXEC Microsoft Windows Installer
MSINFO Windows NT diagnostics
MSTSC Terminal Server Connection (Remote Desktop Protocol)
MUNGE Find and Replace text within file(s)
MV Copy in-use files
NET Manage network resources
NETDOM Domain Manager
NETSH Configure network protocols
NETSVC Command-line Service Controller
NBTSTAT Display networking statistics (NetBIOS over TCP/IP)
NETSTAT Display networking statistics (TCP/IP)
NOW Display the current Date and Time
NSLOOKUP Name server lookup
NTBACKUP Backup folders to tape
NTRIGHTS Edit user account rights
PATH Display or set a search path for executable files
PATHPING Trace route plus network latency and packet loss
PAUSE Suspend processing of a batch file and display a message
PERMS Show permissions for a user
PERFMON Performance Monitor
PING Test a network connection
POPD Restore the previous value of the current directory saved by PUSHD
PORTQRY Display the status of ports and services
PRINT Print a text file
PRNCNFG Display, configure or rename a printer
PRNMNGR Add, delete, list printers set the default printer
PROMPT Change the command prompt
PsExec Execute process remotely
PsFile Show files opened remotely
PsGetSid Display the SID of a computer or a user
PsInfo List information about a system
PsKill Kill processes by name or process ID
PsList List detailed information about processes
PsLoggedOn Who's logged on (locally or via resource sharing)
PsLogList Event log records
PsPasswd Change account password
PsService View and control services
PsShutdown Shutdown or reboot a computer
PsSuspend Suspend processes
PUSHD Save and then change the current directory
QGREP Search file(s) for lines that match a given pattern.
RASDIAL Manage RAS connections
RASPHONE Manage RAS connections
RECOVER Recover a damaged file from a defective disk.
REG Registry: Read, Set, Export, Delete keys and values
REGEDIT Import or export registry settings
REGSVR32 Register or unregister a DLL
REGINI Change Registry Permissions
REM Record comments (remarks) in a batch file
REN Rename a file or files.
REPLACE Replace or update one file with another
RD Delete folder(s)
RDISK Create a Recovery Disk
RMTSHARE Share a folder or a printer
ROBOCOPY Robust File and Folder Copy
ROUTE Manipulate network routing tables
RUNAS Execute a program under a different user account
RUNDLL32 Run a DLL command (add/remove print connections)
SC Service Control
SCHTASKS Create or Edit Scheduled Tasks
SCLIST Display NT Services
ScriptIt Control GUI applications
SET Display, set, or remove environment variables
SETLOCAL Control the visibility of environment variables
SETX Set environment variables permanently
SHARE List or edit a file share or print share
SHIFT Shift the position of replaceable parameters in a batch file
SHORTCUT Create a windows shortcut (.LNK file)
SHOWGRPS List the NT Workgroups a user has joined
SHOWMBRS List the Users who are members of a Workgroup
SHUTDOWN Shutdown the computer
SLEEP Wait for x seconds
SOON Schedule a command to run in the near future
SORT Sort input
START Start a separate window to run a specified program or command
SU Switch User
SUBINACL Edit file and folder Permissions, Ownership and Domain
SUBST Associate a path with a drive letter
SYSTEMINFO List system configuration
TASKLIST List running applications and services
TIME Display or set the system time
TIMEOUT Delay processing of a batch file
TITLE Set the window title for a CMD.EXE session
TOUCH Change file timestamps
TRACERT Trace route to a remote host
TREE Graphical display of folder structure
TYPE Display the contents of a text file
USRSTAT List domain usernames and last login
VER Display version information
VERIFY Verify that files have been saved
VOL Display a disk label
WHERE Locate and display files in a directory tree
WHOAMI Output the current UserName and domain
WINDIFF Compare the contents of two files or sets of files
WINMSD Windows system diagnostics
WINMSDP Windows system diagnostics II
WMIC WMI Commands
XCACLS Change file permissions
XCOPY Copy files and folders